Environmental Sensitivities in Australians and the impacts of these conditions on their lives.
ANRES Data for 137 Registrants – June 2016
We are asking people to register their Environmental Sensitivities. We have 137 registered but we have yet to reach many of the people with Environmental Sensitivity conditions including those with Electromagnetic Hypersensitivity (EHS/ES) who have trouble accessing computers and the internet.
Environmental Sensitivity Conditions listed on ANRES
- MCS – Multiple Chemical Sensitivity;
- CFS/ME – Chronic Fatigue Syndrome/ Myalgic Encephalomyelitis;
- EHS/ES – Electromagnetic Hypersensitivity/Electro-sensitivity;
- Lyme Disease and/or its co-infections;
- Biotoxin-related illness;
- Fibromyalgia;
- Food Sensitivity;
- Fragrance Sensitivity
Results
Number of Conditions
Many people with Environmental Sensitivity have conditions that overlap and co-exist. Those registering are able to select more than one Environmental Sensitivity condition.
The numbers of conditions that registrants selected are represented as percentages of those reporting 1 condition to the maximum of 6 conditions, as shown in Table 1 below.
Table 1 Number of Conditions
| Number of Environmental Sensitivity Conditions | ||
| Number of Conditions | People | % |
| 1 | 13 | 9.5% |
| 2 | 31 | 22.6% |
| 3 | 35 | 25.5% |
| 4 | 28 | 20.4% |
| 5 | 15 | 10.9% |
| 6 | 13 | 9.5% |
| 7 | 1 | 0.7% |
| 8 | 0 | 0.0% |
Over 90% of registrants reported having two or more conditions.
Of those selecting one condition 7 reported EHS/ES, 2 reported Fragrance Sensitivity and one each for Lyme Disease, CFS/ME, MCS and Food Sensitivity.
Environmental Sensitivity Conditions
The most selected conditions so far from the registrants are MCS (75.3%), Food Sensitivity (65.0%), Fragrance Sensitivity (72.3%), EHS (48.2%) and CFS (35.8%), as shown in Table 2 below.
| As the registrants were able to select several conditions the calculated percentages do not add up to 100%. |
Table 2 Environmental Sensitivities selected by Registrants
| Environmental Sensitivity Conditions | Number of Registrants | % |
| MCS | 103 | 75.2% |
| Fragrance Sensitivity | 99 | 72.3% |
| EHS | 66 | 48.2% |
| Food Sensitivity | 89 | 65.0% |
| CFS/ME | 49 | 35.8% |
| Fibromyalgia | 29 | 21.2% |
| Lyme disease &/or its co-infections | 9 | 6.6% |
| Biotoxin-related Illness | 7 | 5.1% |
| Other | 34 | 33.0% |
Common Environmental Sensitivity Co-Conditions
The most common co-conditions are shown in the following Table 3.
MCS – The most commonly selected co-conditions are Fragrance Sensitivity (87.4%) and Food Sensitivity (75.7%), EHS/ES (43.7%) and CFS (41.7%), shown in Table 3.
EHS/ES – The most commonly selected co-conditions are MCS (68.2%), Food Sensitivity (62.1%) Fragrance Sensitivity (60.6%), shown in Table 3.
CFS/ME – The most commonly selected co-conditions are MCS (87.8%), Food Sensitivity and Fragrance Sensitivity (79.6%), and EHS (51.0%) shown in Table 3.
Fibromyalgia – The most commonly selected co-conditions are MCS (79.3%), CFS (75.9%) and Food and Fragrance Sensitivities (79.3%), shown in Table 3
Fragrance Sensitivity – The most commonly selected co-conditions are MCS (90.9%) and Food Sensitivity (75.8%) shown in Table 3.
Food Sensitivity – The most commonly selected co-conditions are MCS (87.6%) and Fragrance Sensitivity (84.2%) shown in Table 3.
Table 3 Environmental Sensitivity Co-conditions
| Environmental Sensitivity Condition | Co-Conditions (Percentage of those with the condition) | |||||
| MCS | CFS | EHS | Fibromyalgia | Fragrance Sensitivity | Food Sensitivity | |
| MCS | — | 41.7% | 43.7% | 23.2% | 87.4% | 75.7% |
| CFS | 87.8% | — | 51.0% | 44.9% | 79.6% | 79.6% |
| EHS | 68.2% | 37.9% | — | 21.2% | 60.6% | 62.1% |
| Fibromyalgia | 79.3% | 75.9% | 48.3% | — | 79.3% | 79.3% |
| Fragrance Sensitivity | 90.9% | 39.4% | 40.4% | 23.2% | — | 75.8% |
| Food Sensitivity | 87.6% | 43.8% | 46.1% | 25.8% | 84.2% | — |
Hardships and difficulties encountered by those with Environmental Sensitivities.
During the course of analysing registrants’ comments it became clear that we needed to include a question regarding the hardships or difficulties they were experiencing. We have included a question that asks if they have hardships or difficulties in the following areas:
1) Medical Assistance,
2) Housing,
3) Education,
4) Employment/Income,
5) Accessing Social Services,
6) Accessing Public places,
7) Relationships/Social Interactions and
8) Other problems.
Hardships selected.
We have 65 responses to this question. The hardships selected are shown below in Table 4. The most selected areas of hardship were Relationships/Social Interaction (87.7%), Medical assistance (78.5%), Employment/Income (76.9%), Accessing public places (72.3%), Housing (66.2%) and Education (52.3%).
Table 4 Hardships
| Hardship | Number of Registrants | % |
| Medical assistance | 51 | 78.5% |
| Housing | 43 | 66.2% |
| Education | 34 | 52.3% |
| Employment/Income | 50 | 76.9% |
| Social Services | 31 | 47.7% |
| Accessing public places | 47 | 72.3% |
| Relationships/social interactions | 57 | 87.7% |
| Other | 27 | 41.5% |
| Total answered | 65 |
Other Hardships
The other areas that individuals indicated they have difficulties with were generally an extension of accessing public places due to exposures to fragrance, other chemicals or electromagnetic radiation.
- Public transport/travel
- Tradespeople
- Shopping
- Eating out/Restaurants
- Public conveniences
- Hospitals
- Personal care (eg haircut)
- Wi-fi exposure
- Mobile phone exposure
- Cinema, community events and organisations
- Housework and home maintenance
- Outdoor markets are full wireless transmissions from cell phones, cell phone tower and eftpos
- Accessing aged care facility
- Gardening, day-to-day activities, finding suitable clothing
- Caring for school-aged children
Number of Hardships
The number of hardships that individuals encounter in their daily lives is shown in Table 4 below.
Approximately 80% of people selected 4 or more areas of hardship.
Table 4 Number of Hardships
| Number of hardships | Number of Registrants | % |
| 1 | 3 | 4.6% |
| 2 | 4 | 6.2% |
| 3 | 6 | 9.2% |
| 4 | 13 | 20.0% |
| 5 | 8 | 12.3% |
| 6 | 9 | 13.8% |
| 7 | 11 | 16.9% |
| 8 | 11 | 16.9% |
Hardships selected by conditions
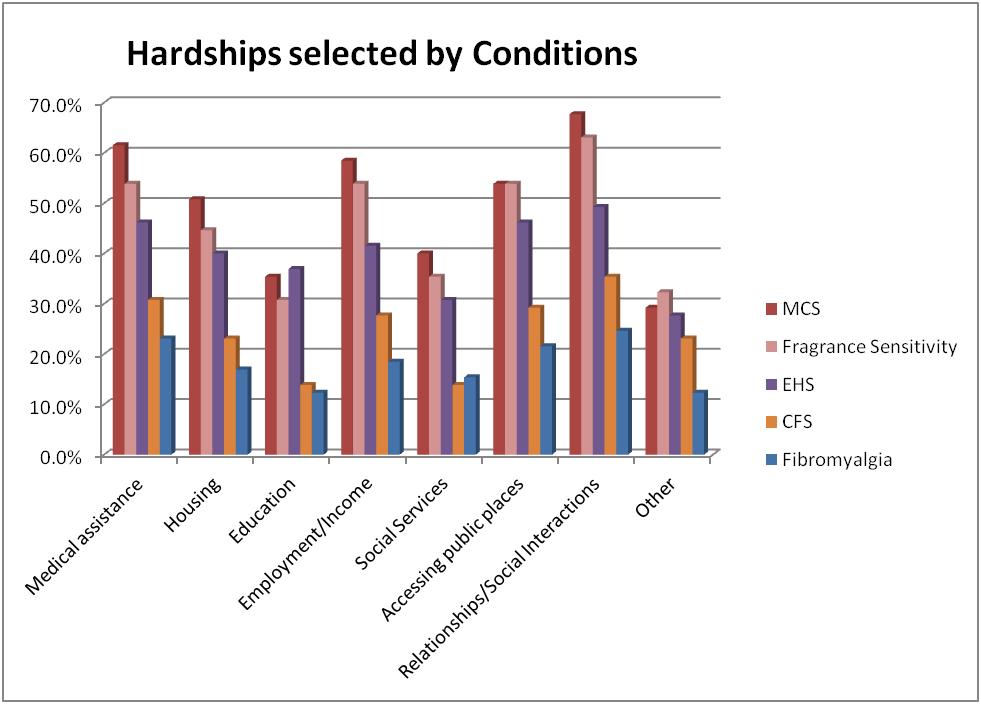
The conditions where most hardships were selected are shown in Table 5 and figure 1 below.
Table 5 Hardship selected by Environmental Sensitivity Condition
| Hardship | MCS and Hardship (%) | EHS and Hardship (%) | CFS and Hardship (%) | Fragrance Sensitivity (%) | Fibromyalgia
(%) |
| Medical assistance | 61.5% | 46.2% | 30.8% | 53.8% | 23.1% |
| Housing | 50.8% | 40.0% | 23.1% | 44.6% | 16.9% |
| Education | 35.4% | 36.9% | 13.8% | 30.8% | 12.3% |
| Employment/Income | 58.5% | 41.5% | 27.7% | 53.8% | 18.5% |
| Social Services | 40.0% | 30.8% | 13.8% | 35.4% | 15.4% |
| Accessing public places | 53.8% | 46.2% | 29.2% | 53.8% | 21.5% |
| Relationships/Social Interactions | 67.7% | 49.2% | 35.4% | 63.1% | 24.6% |
| Other | 29.2% | 27.7% | 23.1% | 32.3% | 12.3% |
The conditions associated with most hardships are MCS, Fragrance Sensitivity and EHS/ES.
Figure 1 Hardship selected by Environmental Sensitivity Condition
Comments on Hardships
Medical
Physical Barriers
- Lack of a safe environment – Issues with chemicals and EMR exposure in consulting rooms.
Lack of Knowledge of Environmental Sensitivities amongst Medical Professionals
- A lack of understanding of the condition and the consequences of a chemical or EMR exposure to the individual by medical staff. When making an effort to avoid triggers that cause adverse health effects people feel that staff are not taking their concerns seriously and consequently suffer from exposures. There are no safe environments (chemical and EMR free) for people to wait for appointments.
- Lack of knowledge by GPs and Specialists. There are few GPs or Specialists who are knowledgeable about Environmental Sensitivities. Those who are knowledgeable are often expensive, do not bulk bill, and Skype and Phone Consultations do not attract a Medicare rebate.
- Many have seen multiple GPs and Specialists with no diagnosis or effective treatments and have given up.
- Misdiagnosis and inappropriate and harmful treatments. “Took over 25 years to diagnose ES and was by then a Universal reactor stage. Was treated badly by medical professionals and told symptoms were in their head. Psychiatric and psychological treatments made symptoms worse with medications producing horrendous side effects – was pumped with more. PLEASE STOP THIS MEDICAL MADNESS”
- Others have taken years for a diagnosis by which time they are severely disabled.
Some have found alternative therapies to help and many have by necessity researched their condition to find a diagnosis and means to improve their lives. “There are no pills for these ills. And that is a blessing in disguise because I’ve found that holistic living (diet, exercise, lifestyle upgrades) make it possible for me to have hope.”
Housing
There were difficulties finding affordable safe housing away from sources of EMR and free from chemical triggers in building materials, paint, new carpets and pest treatments.
Other location issues were:
- Neighbours use of chemicals and/or Wi-Fi devices
- Proliferation of Mobile phone towers
- Proliferation of Wi-Fi hotspots
- 4GX mobile transmission (SE Queensland)
- Smart Meters. Some registrants have had to move from Victoria to other states after the installation of Smart Meters that they report adversely affected their health and triggered or exacerbated their EHS.
Where unemployment has resulted from developing their condition they have no money and are unable to move and either buy their own home or rent.
Others feel they are stuck where they are despite their issue/problems with proximity of phone towers, hot spots or chemical usage. They do not have the money or resources to move and do not know where to move to.
Employment/Income
There were comments that the proliferation of chemicals and EMR in the workplace has meant that they cannot work, or made redundant after disclosing sensitivities. Most felt they were now unemployable.
Environmental Sensitivity Conditions are not understood in the community and consequently people are not being believed and suffering ridicule and bullying as a result.
For one who is trying to manage in the workplace – “I suffer daily in my workplace…. they do not take it seriously and I feel victimised, bullied by certain people occasionally and very isolated. I have even been told by my Leader maybe this isn’t the job for you.”
Education
Education facilities and libraries are increasingly using new wireless technology. For those with EHS these facilities using Wi-Fi technology are unavailable to them.
For those with MCS the prevalence of perfumes and other chemicals were found to be a barrier.
Two secondary school aged children who are very sensitive to EMR may need to be home-schooled in order to avoid it.
Social Services
- There were difficulties in attending Centrelink offices due to use of chemicals and EMR exposures.
- As there is no recognition of Environmental Sensitivities Disability Support pensions are not accessible.
- Unable to obtain a medical certificate or letter from a GP to support their case.
Accessing Public Places
- For both employment and accessing public places there is the issue of accessibility to a safe environment.
- Most public places are inaccessible to some degree. The barriers include chemical use (particularly high levels of fragrance, cleaning chemicals, pesticide etc) and EMR exposures from mobile phones and Wi-Fi technology. This includes libraries, Medicare and Centrelink offices, hospitals, shops, cinema, churches, government buildings and council chambers to name a few.
- To avoid these debilitating exposures people stay at home and are housebound and isolated.
- Where possible people used online services for shopping.
- Many parks, beaches and other external environments are inaccessible due to regular use of glyphosate and other herbicides and EMF from mobile phone towers, Telstra Air and free Wi-Fi hotspots.
- There are also problems with cigarette smoke, new furniture, new carpet, cleaning fluids, printers, fragrances, air fresheners, diesel fumes.
Relationships/ Social Interactions
A large number of people have little to no social interactions and have difficulty forming or maintaining relationships due to the complex nature of their conditions and a lack of understanding by the general population.
Some are particularly isolated from the public, family and friends, and are no longer able to work.
Even when family and friends do acknowledge the problem and not wear a perfume, there are other layers of fragrance. The use of soaps, shampoos, conditions, deodorants and washing machine products all leave traces of fragrance that makes it difficult for others to comply. They often cannot smell the background levels of fragrance that these products leave.
The use of Wi-Fi and mobile phone usage is ubiquitous in the community. Family, friends and visitors often carry a mobile phone and have them switched on.
Isolation was a common theme.
Conclusion
The exposures common to most workplaces and public spaces that people with Environmental Sensitivities must avoid include:
- Chemicals such as pesticides, paints, vehicular emissions, heating system emissions, copier fumes, off-gassing from remodelling or reconstruction and contaminants from other workers’ personal care products including perfumes.
- Electromagnetic field sources including mobile phones and other wireless technology, office equipment, fluorescent lighting, and other sources.
Chemical and electromagnetic exposures have radically changed the quality of life for those with chemical, fragrance and/or EMR sensitivities. Isolation and social exclusion is brought about by the barriers (chemical, electromagnetic, attitudinal, economic) to accessing medical care, education, work, transport, housing, welfare and recreation for those who must avoid chemicals and/or EMRs. Disability is exacerbated by the lack of medical assistance and resources.
Communities fail to consider chemicals and EMR as a barrier to participation in society. For what is not recognised or well understood there is a tendency to ignore, minimise the importance of, ridicule or deny outright. This leads to discrimination in work, medical care, and community access and results in problems with finances, relationships and sense of identity for people attempting to avoid exposure.
The medical model of disability means that GPs are often required to have an input on access to social welfare payments. This medical mandate, combined with the lack of knowledge of toxic-induced illness among providers, is a serious barrier to people with Environmental Sensitivities and contributes to the disabling effects of chemical and electromagnetic barriers.
People with Environmental Sensitivities are not seen as disabled in our modern society. The invisible nature of these conditions allows others to ignore it. For those with Environmental Sensitivities there is repeated mental and physical suffering when trying to access places and services which the majority of the population take for granted.